
Polyhedral Boranes:
Molecules and Ions Central to our Research
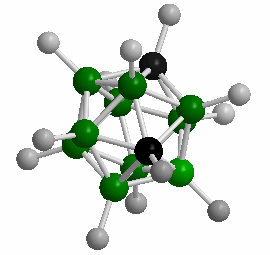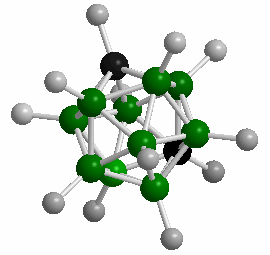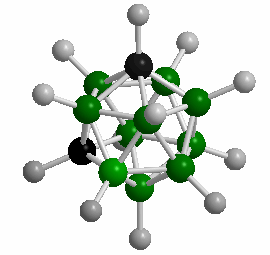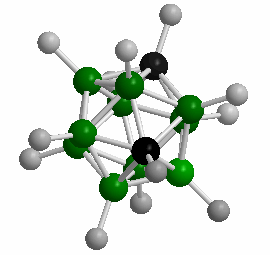
Polyhedral Boranes are a large class of ions and molecules containing:
-
boron and hydrogen
-
boron, carbon, and hydrogen
-
other heteroatoms
Many of the polyhedral boranes were developed as rocket and jet fuel during the 1950’s. While the smaller polyhedral boranes are toxic and highly reactive, the closo 10- and 12-vertex species exhibit remarkably high thermal stability and resistance to oxidative degradation. The sodium salts of these ions exhibit toxicities lower than that of table salt! In addition to the formation of conventional bonds, atypical bonding extensively occurs within these clusters: the formation of three-center, two-electron bonds. Extensive delocalization of framework bonding electrons results in interesting electronic properties for these species.
Our group’s research focuses on potential biomedical, analytical, and material science applications of the polyhedral boranes.
The closo-dodecaborate anion [B12H12]^2- exhibits extraordinarily high thermodynamic stability. For example, salts of this cluster containing inert cations are stable in vacuum to 900°C; it is also stable in solutions of hot concentrated hydrochloric acid or potassium hydroxide. Such stability results in low biological toxicities for this cluster, but it also renders them relatively inert to many chemical reactions. As such, today there are few real-world applications for these substances.
Recently, our group reported a new class of organic-inorganic hybrid materials: polyarylboranes. Remarkably, in the absence of any catalyst, the dodecaborate ion reacts directly with a wide range of mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. In polyarylboranes, the dodecaborate ion serves as a reactive core upon which several aryl ligands are bound through stable boron-carbon bonds. Many of these species exhibit remarkable electronic properties, including high fluorescence quantum yields. Our group is currently exploring and expanding the scope of known substitution chemistry of these polyarylboranes, focusing on potential applications in bioimaging, alternative energy and materials science.
Polyarylboranes


Syntheses of polyarylboranes
9-fold polyphenylborane
Boron-based Drug Discovery
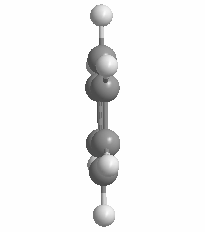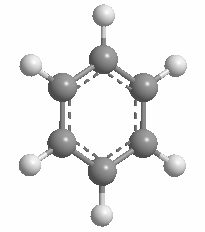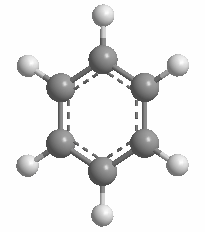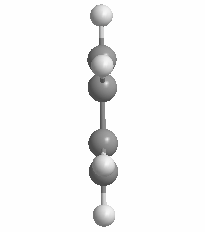
The volume of the 12-vertex borane approximates that of a benzene ring rotated about 180°.

Using carboranes, our group has developed a class of highly potent anticancer agents which exhibit sub-nanomolar activity against a wide range of human cancer cell lines in vitro. These small molecules are potent inhibitors of the enzyme nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt), which regulates the first and rate-limiting step of the NAD+ recycling pathway.
The enzyme Nampt has implications in a wide-range of diseases, including cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, and diabetes. We are currently developing a class of cancer-specific targeted prodrugs of these exceptionally potent molecules.
